SCLERODERMA IS A GROUP OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE DISEASES
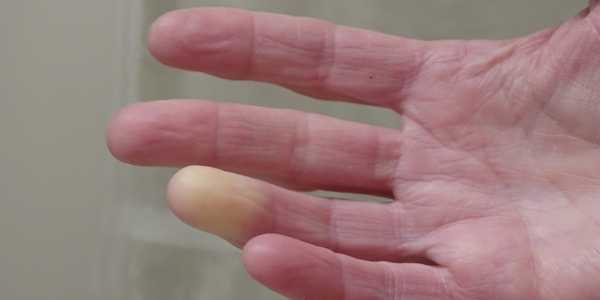
Scleroderma is a group of diseases that affect the body’s connective tissue, which supports the skin and internal organs. Skin, blood vessels, or other tissues may become hard or thick. Swelling or pain may arise in muscles and joints.
Scleroderma can occur in people of all ages, races, and ethnic groups. For unknown reasons, it’s more common in women than men.
Scleroderma symptoms vary widely and are similar to other diseases. This can make the condition hard to diagnose. There are 2 main types: localized and systemic.
Localized scleroderma usually affects only the skin, which becomes hard and tight. It may improve without treatment. But severe cases can leave skin damaged.
Systemic scleroderma is often more serious. It can affect the skin, tissues under it, blood vessels, and major organs, such as the heart, lungs, and kidneys.
Scientists are not yet certain what causes scleroderma. It sometimes runs in families. But it also occurs in people without a family history of the disease. Scleroderma isn’t contagious, so you can’t “catch” the disorder from someone who has it.
Article Source
1. National Institutes of Health (NIH), USA.